It have been proved that reducing cable diameters and increasing connection densities offered by fiber links would be extremely valuable during installation in constrained space, like data center, large enterprise equipment rooms, central office, etc. With the market turning to 40/100G transmission, to reduce congestion during cabling and make it easier to organize equipment cable runs, the network designers turns to MPO/MTP technology and components for today's duplex fiber transmission. Then, network designers face another challenge which is how to assure the proper polarity of these array connections using MPO/MTP components from end-to-end.
Traditionally, a fiber optic link requires two fibers for full duplex communications. It is very important to ensure that the equipment on the link are connected properly at each end. However, when the link contains two or more fibers, maintain the correct polarity across a fiber network become more complex, especially when using multi-fiber MPO components for high data rate transmission. Luckily, pre-terminated MPO components adopt humanized design for polarity maintenance and the TIA 568 standard provides three methods for configuring systems to ensure that proper connections are made. This article will introduce polarity in MPO system and 40/100GbE polarization connectivity solutions in details.
Polarity in MPO Components
To maintain the correct polarity in MPO systems, the property of the components of MPO systems should be understood firstly. This part will introduce the basic components that are used in MPO system.
MPO Connector: To understand the polarity in 40/100 GbE transmission, the key of MPO technology—MPO connector should be first introduced. MPO connector usually has 12 fibers. 24 fibers, 36 fibers and 72 fibers are also available. Each MTP connector has a key on one of the flat side added by the body. When the key sits on the bottom, this is called key down. When the key sits on the top, this is referred to as the key up position. In this orientation, each of the fiber holes in the connector is numbered in sequence from left to right and is referred as fiber position, or P1, P2, etc. A white dot is additionally marked on one side of the connector to denote where the position 1 is. (shown in the following picture) The orientation of this key also determines the MTP cable's polarity.
MPO Adapter: MPO (male) connectors are mated to MPO(female) connectors using a MPO adapter. As each MPO connector has a key, there are 2 types of MPO adapters:
Type A—key-up to key-down. Here the key is up on one side and down on the other. The two connectors are connected turned 180° in relation to each other.Type B—key-up to key-up. Here both keys are up. The two connectors are connected while in the same position in relation to each other.
MPO Cables: MPO trunk cable with two MPO connectors (male/female) on both side of the cable serves as a permanent link connecting the MPO modules to each other, which is available with 12, 24, 48, 72 fibers.
MPO harness cable, which is terminated with a male/female connector on the MPO side and several duplex LC/SC connectors on the other side, provides a transition from multi-fiber cables to individual fibers or duplex connectors.
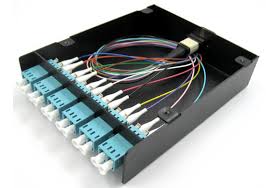
MPO Cassette: Modular MPO cassette is enclosed unit that usually contains 12 or 24-fiber factory terminated fan-outs inside. It enables the user to take the fibers brought by a trunk cable and distribute them to a duplex cable with a MPO connector (at the rear) to the more common LC or SC interface (on the front side). The following is a MTP cassette with 6 duplex LC interface and a MTP connector.
Three Cables for Three Polarization Methods
The three methods for proper polarity defined by TIA 568 standard are named as Method A, Method B and Method C. To match these standards, three type of MPO truck cables with different structures named Type A, Type B and Type C are being used for the three different connectivity methods respectively. In this part, the three different cables will be introduced firstly and then the three connectivity methods.
MPO Trunk Cable Type A: Type A cable also known as straight cable, is a straight through cable with a key up MPO connector on one end and a key down MPO connector on the opposite end. This makes the fibers at each end of the cable have the same fiber position. For example, the fiber located at position 1 (P1) of the connector on one side will arrive at P1 at the other connector. The fiber sequence of a 12 fiber MPO Type A cable is showed as the following:
MPO Trunk Cable Type B: Type B cable (reversed cable) uses key up connector on both ends of the cable. This type of array mating results in an inversion, which means the fiber positions are reversed at each end. The fiber at P1 at one end is mated with fiber at P12 at the opposing end. The following picture shows the fiber sequences of a 12 fiber Type B cable.
MPO Trunk Cable Type C: Type C cable (pairs flipped cable) looks like Type A cable with one key up connector and one key down connector on each side. However, in Type C each adjacent pair of fibers at one end are flipped at the other end. For example, the fiber at position 1 on one end is shifted to position 2 at the other end of the cable. The fiber at position 2 at one end is shifted to position 1 at the opposite end etc. The fiber sequence of Type C cable is demonstrated in the following picture.
Three Connectivity Methods
Different polarity methods use different types of MTP trunk cables. However, all the methods should use duplex patch cable to achieve the fiber circuit. The TIA standard also defines two types of duplex fiber patch cables terminated with LC or SC connectors to complete an end-to-end fiber duplex connection: A-to-A type patch cable—a cross version and A-to-B type patch cable—a straight-through version.
The following part illustrates how the components in MPO system are used together to maintain the proper polarization connectivity, which are defined by TIA standards.
Method A: the connectivity Method A is shown in the following picture. A type-A trunk cable connects a MPO module on each side of the link. In Method A, two types of patch cords are used to correct the polarity. The patch cable on the left is standard duplex A-to-B type, while on the right a duplex A-to-A type patch cable is employed.
Method B: in Connectivity Method B, a Type B truck cable is used to connect the two modules on each side of the link. As mentioned, the fiber positions of Type B cable are reversed at each end. Therefore standard A-to-B type duplex patch cables are used on both sided.
Method C: the pair-reversed trunk cable is used in Method C connectivity to connect the MPO modules one each side of the link. Patch cords at both ends are the standard duplex A-to-B type.
Upgrade to 40/100GbE With Correct Polarity
The using of MPO/MTP connectors for 40/100G transmission is achieved with multimode fiber by transmitting multiple parallel 10G transmissions that will then be recombined when received. This method has been standardized. The following is to offer 40G transmission solution and 100G respectively.
40G Transmission Connectivity
The 40G transmission usually uses 12-fiber MPO/MTP connectors. There are eight lanes within twelve total positions being employed for transmitting and receiving signals. Looking at the end face of the MPO/MTP connector with the key on top, the four leftmost positions are used to transmit, the four rightmost positions are used to receive, the four in the center are unused. The following picture shows the optical lane assignments. (Tx stands for Transmit, Rx stands for Receive) This approach would transmit 40G using for parallel 10G lanes in each direction according to 40GBase-SR4.
100G Transmission Connectivity
The 100G transmission over multimode requires a total of 20 fibers, 10 for transmitting and 10 for receiving. There are three options which is introduced as following:
The first method is to use a 24-fiber MPO/MTP connector with the top center 10 positions allocated for receiving and the bottom 10 position allocated for transmitting,as shown in the following figure. This method is recommended by IEEE.
The second option is to use two 12-fiber MPO/MTP connectors side by side. The 10 positions in the center of the connector on the left are used for transmitting and the center 10 positions of the left are used for receiving.
The third way of 100G transmission also uses two 12-fiber MPO/MTP connectors, but it uses the stacked layout as showed in the following figure. The ten center positions of the top connector are used for receiving and the ten center position of the bottom are used for transmitting.
Understand Polarity in 40/100G
Any transmit position should be connected to its own receive position. Here's an analogy to illustrate: Think of ball players. You have pitchers & catchers. For 10G transmission, Pitcher 1 needs to throw to Catcher 1, Pitcher 2 to Catcher 2 and so on. (showed on the left side of the following picture) For 40/100G, any pitcher can throw to any catcher.(showed on the right side of the following picture)
But if you've got two catchers looking at each other as showed in the following picture, there isn't a whole lot happening.
Conclusion
Network designer using MPO/MTP components to satisfy the increasing requirement for higher transmission speed, during which one of the big problems—polarity, can be solved by selecting the right types of MPO cables, MPO connectors, MPO cassette and patch cables. Consider the polarity method to be used and selecting the correct MPO/MTP components to support that methods, the proper solution for 40/100G transmission would be achieved with high density and flexibility and reliability.
Read more »