Optics and Cables Selection for Storage Area Network (SAN)
Optics and cables are the most important infrastructures of network connectivity. In a storage area network (SAN), switches are used between servers and storage devices. This means that you should make connection with optics and cables between the server and switch, storage and switch as well as the switch and switch. Of course, according to different application environments, you should choose different optics and cables in order to get the best performance. Furthermore, you may need to consider the future expansion of your network. Thus, an economical and effective solution of optics and cables are very necessary.
Key Factors Influencing Your Decision
Firstly, there are some key factors which will influence your decision. Thus, you must make sure that what your network really requires. As we mentioned above, an SAN has server, storage device and switches. So, what should we consider in every section of the network?
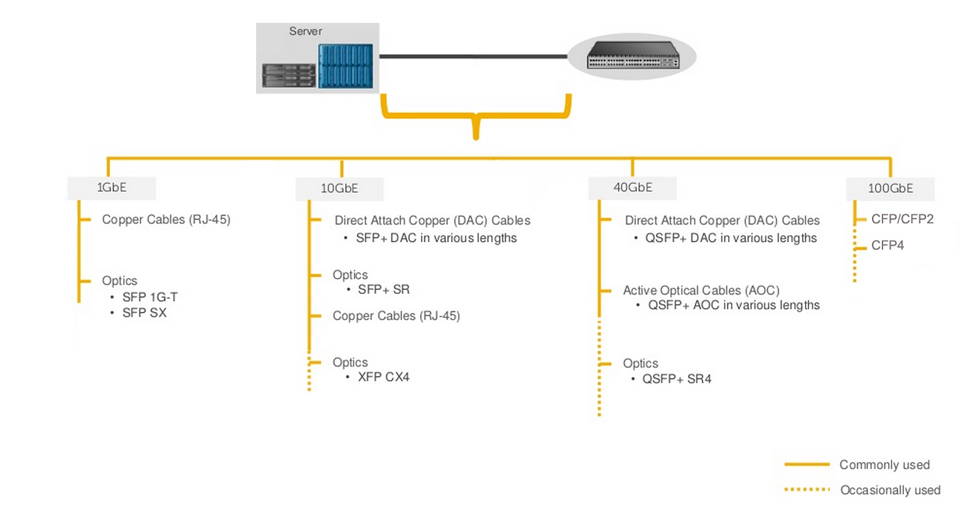
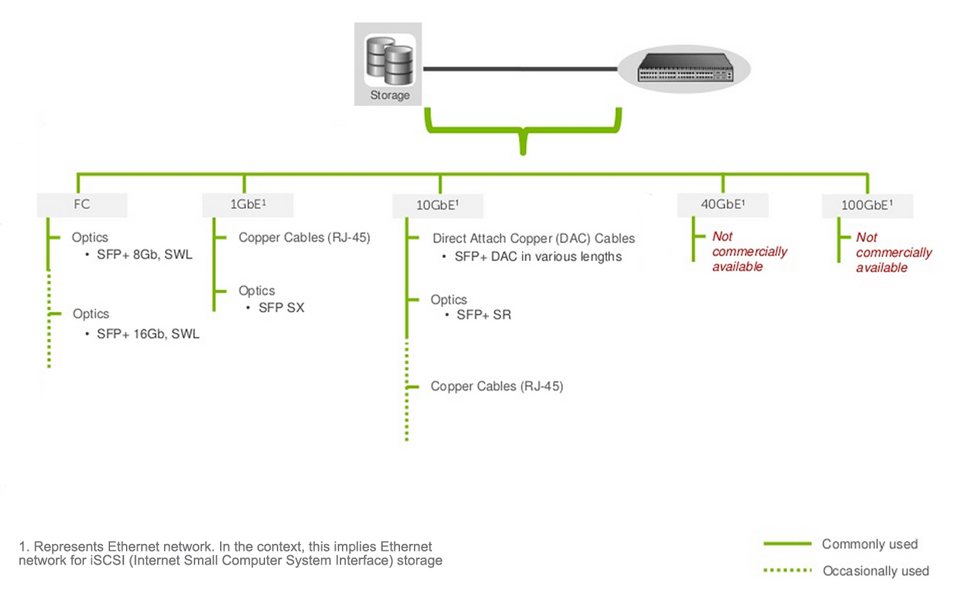
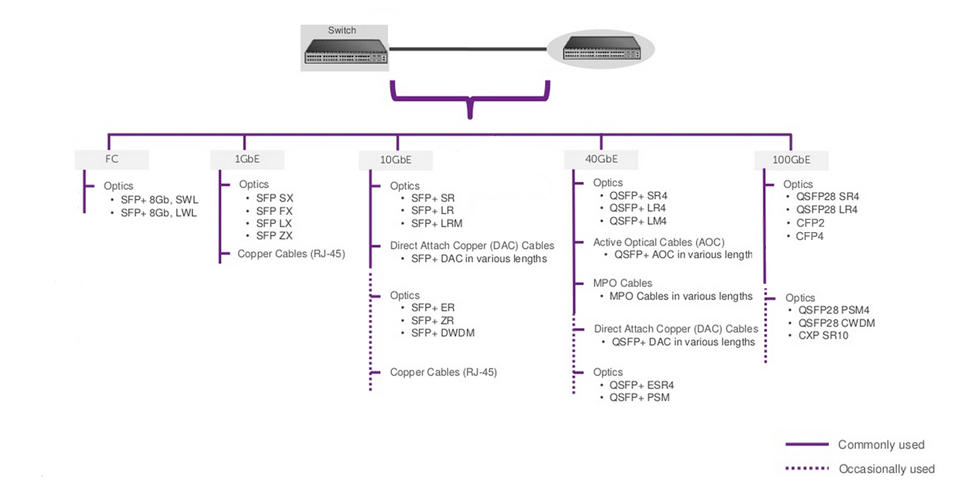
Bandwidth: Depending on the application load requirements, customers typically decide whether they want 1GbE, 10GbE, or 40GbE. In some cases, the decision may also be dictated by the type of traffic, e.g. DCB (Data center bridging) requires 10GbE or higher.Cost: Servers claim the highest share of devices deployed in any data center. Choosing a lower cost connectivity option results in a much lower initial deployment cost.Power: In any high density server deployment, a connectivity option which consumes lower power results in much lower OpEx.Distance: Servers are typically connected to a switch over a very short distance, i.e. typically within the same rack or, in some cases, within the same row.Cabling Flexibility: Some customer prefer to make their own copper cables due to variable distance requirement. This requirement limits the choice of connectivity to copper cables only.
Reliability: Typical storage traffic is very sensitive to loss. Even a minor loss of traffic may result in major impact on application performance.Qualification: Storage vendor qualification or recommendation plays an important role in this decision due to reasons such as customer support, peace of mind, etc.Latency: Any time spent in transition is time taken away from data processing. Reducing transition time results in much faster application performance. The result may have a direct impact on customers' bottom line, e.g. faster processing of online orders.
Bandwidth: On server facing ports, servers typically dictate the per port bandwidth requirement. However, per port bandwidth requirement for the network facing (switch-to-switch) ports denpends on multiple factors including amount of traffic generated by the servers, oversubscription ratios, fiber limitations, ect.Distance: An inter-switch or switch to router connection could range from a few inches to tens of kilometers. Generally, the price of optics increases as the distance increases.Latency: The network topology and application traffic profile (East-west, HPC (High Performance Computing), computer cluster, etc.) and influence the minimun latency that can be tolerated in the network.
-
Server to Switch Connectivity Solution
-
Storage to Switch Connectivity Solution
-
Switch to Switch Connectivity Solution
COMPUFOX Solutions
COMPUFOX offers a comprehensive solution of optics and cables which supports your network from 1GbE to 100GbE. We have a great selection of 1000BASE-T/SX/LX SFP, BiDi SFP, 10GBASE-SR/LR SFP+, DWDM SFP+, whole series 40G QSFP+ optics and cables, as well as the 100G CFP2 and CFP4, etc. which help you solve the cost issue in fiber project. Especially the 40G QSFP+ optics, with the passive optic design, they can be compatible with all the equipment of all major brands. In addition, most of them are ready stock. See Links below:
- CFP
- CWDM
- DWDM
- GBIC
- QSFP+
- SFP+
- SFP
- X2
- XENPAK
- XFP
- QSFP+ Cables
- QSFP+ to 4 SFP+ Cables
- QSFP+ to 4 XFP Cables
- QSFP+ to 4 LC Cables
- QSFP+ to CX4 Cables
- SFP Cables
- SFP+ Cables
- SFP+ to XFP Cables